Bad data carries significant direct, indirect, and hidden costs across all business functions. Data cleansing mitigates the costs of bad data by improving operational efficiency, decision-making, and customer relations. Investing in data cleansing delivers both immediate and long-term financial benefits.
Contents
Bad data in business leads to misinformed decisions, lost productivity and damage to reputation. These consequences represent the cost of bad data, a hidden expense that can quietly erode a company’s bottom line.
The role of data cleansing in addressing bad data involves identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies and inaccuracies within a dataset. It improves the accuracy and reliability of data used for decision making and enhances operational efficiency. Employees spend less time searching for, correcting or working around bad data, freeing them to focus on more valuable tasks.
Data cleansing also plays a crucial role in raising data quality awareness within an organization. By actively engaging in data cleansing, companies demonstrate a commitment to data quality.
With clean and reliable data, businesses can streamline operations, leading to increased profitability and a competitive advantage.
Understanding the financial costs of bad data
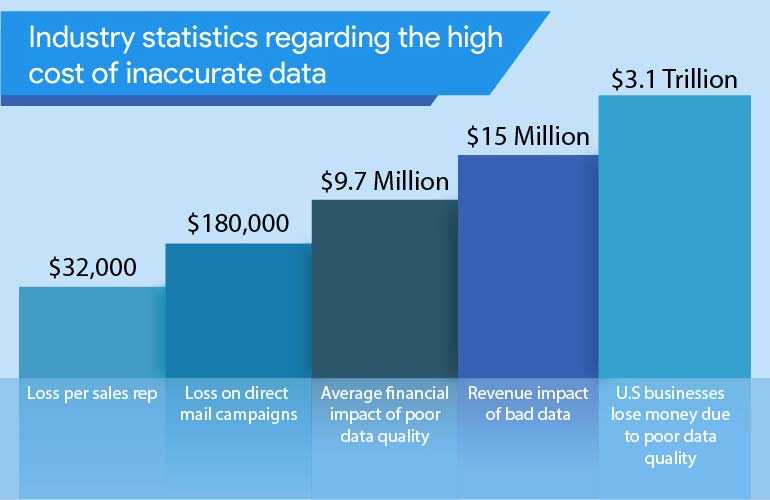
1. Direct costs
Inaccurate data introduces process bottlenecks. These bottlenecks necessitate rework, leading to delays and decreased operational efficiency. The consequences include reduced productivity and elevated operational costs. In marketing, flawed customer data results in poorly targeted campaigns, squandering advertising budgets and missing valuable opportunities.
Further, inaccurate segmentation and personalization initiatives yield low conversion rates and tarnish brand reputations. Organizations frequently underestimate the resources required for data quality remediation. Manual data cleansing, deduplication and error correction demand substantial labor hours and necessitate investments in specialized technology.
These costs, although essential for mitigating the impact of substandard data, constitute a direct financial drain. Proactive data quality management can minimize this drain. Gartner research estimates the average annual loss due to poor data quality at approximately $12.9 million in 2021.
2. Indirect costs
Misinformed strategies are a consequence of bad data. These strategies lead to poorly allocated resources and missed market opportunities. For instance, flawed demand forecasting can cause overstocking or shortages, ultimately impacting profitability.
Inaccurate financial reporting, as an impact of bad data, triggers a series of financial repercussions. Regulatory bodies impose penalties for non-compliance due to misreported figures. Investors depend on accurate financial statements for well-informed decision making. Distorted data leads to poor investment choices, impacting stock valuations and future funding opportunities.
Reputational damage, while challenging to quantify directly, constitutes a substantial indirect cost. Data breaches and privacy violations weaken customer trust, causing attrition and reducing brand loyalty. The lasting impact of a damaged reputation can diminish market share and limit future growth prospects.
3. Hidden costs
Hidden costs drain resources, often hiding in plain sight within normal operations. Consider this: you miss a critical market inflection point because of faulty customer segmentation from bad data. What’s the impact? Lost revenue and market share. Similarly, inaccurate market analysis can easily lead to overstocking, which means storage costs and write-offs.
Reduced agility happens when you can’t respond quickly to market shifts. This is because you’re relying on unreliable data. Migrating data from legacy systems is often a problem. These systems are full of inconsistencies and errors that can cripple real-time decision making. This directly impacts innovation. If you pivot based on flawed data, you waste resources and miss opportunities.
The cost of bad data on major business functions

Data integrity is the foundation of strategic decision making and operational efficiency in modern business. However, inaccurate data infiltrate various business functions, leading to significant financial repercussions and damage to the company’s reputation.
1. Sales and marketing
Lead scoring models fueled by bad data can misallocate resources for sales teams. This can lead to sales teams pursuing low-potential leads while neglecting high-value prospects.
Poor data quality in marketing automation systems can also be detrimental. Incorrect demographic information, for instance, leads to irrelevant targeting. Consider a luxury car manufacturer sending promotional emails for a new sports car to a segment primarily interested in family SUVs.
This misalignment results in low conversion rates, high unsubscribe rates, and potential brand damage. These issues erode brand trust and diminish the effectiveness of future campaigns, thereby impacting long-term revenue streams.
2. Finance and accounting
Inaccurate financial data erodes investor trust, impacts valuation, and triggers legal action. Misrepresented financials create flawed investment strategies that negatively affect portfolio performance. Material misstatements require restatements, which incur audit and legal costs and damage credibility.
For example, consider a company that overstates revenue due to a systemic data-entry error. The stock price plummets upon discovery and correction of the error, as investors lose confidence. This demonstrates a direct link between data integrity and market perception.
Reputational damage from inaccurate data erodes long-term investor relations, affecting future funding opportunities. Inaccurate data negatively affects internal financial planning, leading to suboptimal resource allocation and missed growth opportunities.
3. Supply chain management
Demand forecasts based on flawed data lead to inventory imbalances. Overstocking ties up capital and incurs storage costs, while stockouts result in lost sales and erode customer satisfaction.
Poor data quality does not stay confined to one area. It impacts vendor relationships, logistics and more. Inaccurate BOMs and outdated forecasting models amplify these issues, creating ripple effects throughout the supply chain.
Take the example of a retailer who relies on flawed sales data. If they overestimate demand for a seasonal item, they’ll end up with excess inventory. This often leads to markdowns or writeoffs, directly impacting their bottom line.
4. Other sectors affected by bad data
The following sectors are impacted by inaccurate data as well:
- In aviation, inaccurate flight data cause delays, costing billions in wasted fuels and compensations. Bad data in air traffic control systems lead to disruptions and even hazards such as collisions.
- Healthcare suffers from misdiagnoses due to faulty data, leading to unnecessary procedures and increased costs.
- Public sectors struggle with inefficient resource allocation due to inaccurate census and economic data, leading to mismanaged budgets and ineffective public services.
- HR departments using biased data risk discrimination lawsuits, costing companies millions in settlements and reputational damage.
Learn how to combat bad data costs with effective data cleansing.
Contact our data cleaning experts »Data cleansing importance in cost reduction (Keep as is in the existing article)
Data cleansing, also known as data cleaning or data scrubbing, is the process of identifying, correcting or removing errors, inconsistencies and inaccuracies in datasets. This practice involves various steps, including:
- Data auditing: Assessing the current state of data quality and identifying issues
- Data cleaning: Correcting or removing errors and inconsistencies in the data
- Data validation: Ensuring that cleaned data meets predefined quality standards
- Data monitoring: Continuously tracking data quality to maintain high standards
By implementing data cleansing, businesses can ensure that their data is accurate, consistent and up-to-date, leading to better decision-making and operational efficiency.
A. Overview of data cleansing tools and services
There are various data cleansing tools available in the market, each offering unique features and capabilities to help businesses maintain high-quality data. Some popular data cleansing tools include:
- OpenRefine: An open-source tool for cleaning and transforming data, OpenRefine offers features such as data clustering, faceting and filtering to help identify and correct data issues.
- DataWrangler: A web-based tool for cleaning and reshaping data, DataWrangler provides an intuitive interface for data manipulation and transformation, making it easy for users to address data quality issues.
- Trifacta: A data preparation platform that includes data cleansing capabilities, Trifacta offers advanced features, such as data profiling, pattern recognition, and machine learning-assisted transformations to improve data quality standards.
Though these tools can help businesses save costs, they don’t help to meet customized requirements that your business might have. Outsourcing your data cleansing process to experienced service providers will help in the long run to reduce manual effort and ensure data quality. You can also read about 10 best data cleaning companies here.
B. Steps to integrate data cleansing into your business
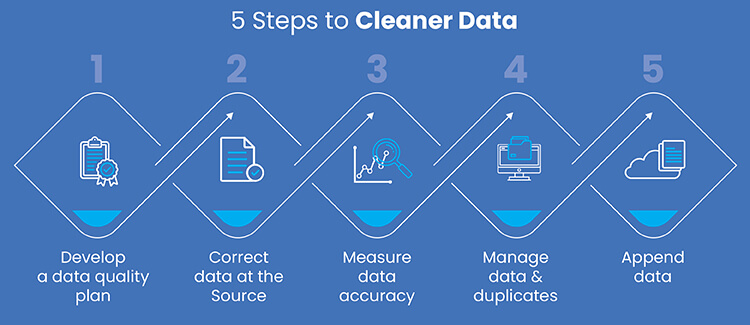
To integrate data cleansing into your business, follow these steps:
- Assess your current data quality: Evaluate the state of your data quality and identify areas for improvement, such as duplicate records, missing values, inconsistent or incorrect data entries, and inconsistent formatting.
- Choose a data cleansing tool or service provider: Select a data cleansing tool or service provider that meets your needs and budget, considering factors such as ease of use, scalability and integration with your existing systems.
- Develop a data cleansing strategy: Establish a data cleansing strategy that outlines your data quality goals, processes and standards as well as the roles and responsibilities of team members involved in data cleansing.
- Implement the data cleansing tool or services: Integrate the chosen data cleansing method into your business processes and systems, ensuring seamless data flow and efficient data management.
- Monitor and maintain data quality: Continuously track data quality and address any emerging data quality issues to maintain high standards and ensure the effectiveness of your data cleansing efforts.
C. Role of training staff in data cleansing to further cost reduction
Training staff in data cleansing techniques and best practices can further reduce costs by:
- Ensuring data quality awareness: Educating employees on the importance of data quality and the consequences of bad data helps create a culture of data quality awareness and adherence to best practices.
- Reducing reliance on internal teams: Training staff in data cleansing techniques can build up on your costs, time and efforts. The need for external consultants or services is crucial to managing data quality, resulting in cost savings.
- Empowering employees to address data quality issues: Equipping employees with the skills and knowledge to identify and address data quality issues proactively helps maintain high-quality data and reduces the costs associated with correcting errors and inconsistencies.
In addition to direct cost savings, data cleansing offers indirect cost savings for businesses:
- Better decision-making: Accurate and reliable data enables businesses to make better informed decisions, leading to cost savings through optimized strategies and reduced risk of costly mistakes.
- Enhanced customer relationship management: Consistent and up-to-date customer information allows businesses to better understand and serve their customers, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty and reduced customer churn costs.
- Improved operational efficiency: High-quality data streamlines business processes and improves productivity, resulting in cost savings through increased efficiency and reduced waste.
With clean data, earn clear profits.
Get a free quote »By integrating data cleansing into your business and training staff in data cleansing techniques, you can directly and indirectly reduce costs, improve decision making, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. Investing in data cleansing. is not only a smart business decision, but also a necessary one.
Case Study

HabileData optimized a lead generation company’s marketing dataM by using advanced web research to build an accurate email list. This included identifying target emails, addressing data decay, delivering clean, validated data, empowering effective campaigns, and enhancing client engagement.
Read the complete story »Benefits of data cleansing
Data cleansing enables cost savings from increased operational efficiency:
- Streamlining data management processes: By identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies and inaccuracies in datasets, data cleansing streamlines data management processes, reducing the time and resources spent on manual data cleaning tasks.
- Reducing storage and processing costs: Eliminating duplicate records and maintaining accurate data can help reduce storage and processing costs, as businesses only need to store and process relevant, high-quality data.
- Improving productivity: High-quality data enables employees to work more efficiently, as they can trust the information they are using and spend less time addressing data quality issues.
It also facilitates cost reduction from improved decision making:
- Enabling better-informed decisions: Clean, high-quality data provides businesses with the information they need to make better-informed decisions, leading to optimized strategies and a reduced risk of costly mistakes.
- Facilitating data-driven insights: Accurate data allows businesses to generate valuable insights through data analysis, enabling them to identify opportunities for cost savings and revenue growth.
Data cleansing gives you cost benefits from enhanced customer relationship management:
- Maintaining consistent and up-to-date customer information: Data cleansing ensures that customer information is accurate, consistent and up-to-date, allowing businesses to better understand and serve their customers.
- Reducing customer churn: High-quality customer data enables businesses to deliver personalized and relevant experiences, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty and reduced customer churn costs.
It helps you avoid costs with better regulatory compliance:
- Maintaining compliance with data protection regulations: Data cleansing helps businesses ensure that their customer data is accurate and up-to-date, reducing the risk of noncompliance with data protection regulations and avoiding potential fines and penalties.
- Avoiding costly audits and investigations: By maintaining high-quality data, businesses can reduce the likelihood of costly audits and investigations related to data quality issues.
Case Study

HabileData annually cleansed and enriched over 17 million records for an American hospitality data aggregator, ensuring 100% accuracy. Leveraging ISO-certified processes, it handled segmentation, validation and auditing, optimizing decision making and delivery within 12-hour cycles.
Read the complete story »The future of data cleansing and cost control
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect several advancements in data cleansing technologies, including:
- Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can be used to automate the data cleansing process, identify patterns and anomalies in data, and make intelligent recommendations for data corrections and improvements.
- Automated data cleansing: AI and machine learning can automate the data cleansing process, reducing manual effort and associated labor costs.
- Improved accuracy and efficiency: AI and machine learning algorithms can identify and address data quality issues more accurately and efficiently than manual processes, leading to cost savings through reduced errors and improved data quality.
By leveraging AI and machine learning in data cleansing, businesses can unlock new cost-saving opportunities and further enhance their overall efficiency.
Wrapping up
The future of data cleansing and cost control holds significant promise. Advancements in data cleansing technologies, along with the integration of AI and machine learning, offer exciting new opportunities to achieve cost savings and enhance business efficiency.
As we embrace these innovations and prioritize data quality to combat the cost of bad data, we position our businesses to maintain a competitive edge and drive growth.
Discover the real cost of bad data and combat it.
Start a conversation »
Savant Fernandez is a marketer and versatile writer who authors content on business process management and market research. He finds his passion in providing valuable insights to his audience on managing and scaling businesses through operational efficiencies and use of technology.






